| |
The Construction: Observation Two
We can apply the notion of duality to what we realized
in observation one. In observation one we found that we could apply Pappus'
theorem six times to each pair of triples of collinear points in the Projective
Plane. The results are six new lines in the plane and we found that of these
six lines, there are two sets of three of them which are coincident.From
what we know of duality, two pairs of triples of coincident lines is dual
to two pairs of triples of collinear points. Thus, we can apply the Dual to
Pappus' theorem to these newly constructed triples of coincident lines and
obtain a point in the plane. Moreover we can permute the construction again
and we will obtain six new points in the plane. We can apply the dual to observation
one and it is obvious that these six points can be broken up into two pairs
of three collinear point.
We will explicitly state the construction thus far.
Let x=(X1
,X2,X3)and
y=(Y1,Y2,Y3) be
two sets of three collinear points. Then let 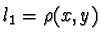 ,
, 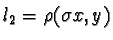 ,
, 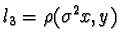 ,
, 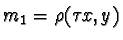 ,
, 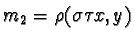 ,and
,and 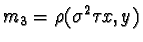 be the lines constructed by permutations of Pappus' Theorem. Observation one
tells us that l1, l2, and l
3are coincident and the lines m1, m2
,and m3 are coincident as well. Let
l=(l1,l2,l3)and
m=(m1,
m2,m3)be triples of coincident lines. Then
we can apply the dual to Pappus' theorem six times to l andm
. Let
be the lines constructed by permutations of Pappus' Theorem. Observation one
tells us that l1, l2, and l
3are coincident and the lines m1, m2
,and m3 are coincident as well. Let
l=(l1,l2,l3)and
m=(m1,
m2,m3)be triples of coincident lines. Then
we can apply the dual to Pappus' theorem six times to l andm
. Let 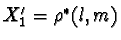 ,
, 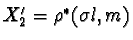 ,
, 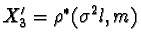 ,
, 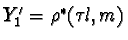 ,
, 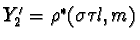 ,and
,and 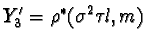 .Then by the dual to Observation One, X'1, X'
2,and X'3 are collinear, as are Y'1
, Y'2,and Y'3.
.Then by the dual to Observation One, X'1, X'
2,and X'3 are collinear, as are Y'1
, Y'2,and Y'3.
We can make another observation in addition to results
provable from observation one.
Observation 2 The triples of points
return to the same line. That is the six pointsX1, X
2,X3,X'1,X'2,
andX'3 all lie on the same line as do Y1
,Y2,Y3,Y'1, Y
'2, andY'3.
An applet demonstrating this observation is shown
below.
Again, you may move the green and the blue points
around the screen. The red points indicate the points X'1
, X'2,X'3,Y'1,Y
'2, andY'3.
The Final Step: Observation 3
|
|
